Updated: 2 April, 2024
Medical simulation centres are a critical tool for the training of medical professionals. Thus, these centres must operate as efficiently and safely as possible to maximise the value they create. In this blog post, we will mostly talk about how to improve medical simulation centres. However, let us first review what they are, their applications, and their main issues.
Key takeaways:
- Medical simulation centres are crucial for practical medical training, offering a risk-free environment for skill development.
- They face challenges like high costs, limited realism, and limited scope in simulating various medical procedures.
- Implementing efficient strategies can mitigate these challenges, focusing on software solutions rather than expensive hardware.
- Videolab and Cloudcontrol offer innovative solutions for medical simulation centres, enhancing training quality and reducing costs.
- These tools provide secure, flexible, and cost-effective alternatives for recording and evaluating medical training sessions.
What is a medical simulation centre?
A medical simulation centre is a place where medical professionals can practice and develop their abilities in a variety of medical procedures and scenarios in a simulated environment.
What are medical simulation centres used for?
Training
Medical simulation centres use high-fidelity mannequins, virtual reality simulations, actors, and other sorts of simulated tools and technology to train medical personnel. This allows trainees to study and improve their abilities in a secure, controlled setting without endangering actual patients.
They are crucial for medical education as practical experience is highly necessary in this field. As one can imagine, doctors need to have numerous hours of practice with medical procedures before they can apply them on patients
Medical simulation centres help in improving doctor patient communication. For example, using simulators or with actors, doctors can practice their communication skills with the patient. These communication skills cover a variety of different practices, from explaining the treatments, to delivering good and bad news, to obtaining information from the patient by asking questions.
Medical Simulation centres develop joint-decision making, another communication practice that doctors need to develop particularly in countries like the Netherlands. The patient participates in medical decisions around their care through joint decision making. Effective joint decision making by doctors, which requires special training, enhances the patient’s physical and psychological well-being.
Evaluation
However, simulation centres not only provide training but also facilitate evaluations. For example, in Spain all students in the last year of their medicine bachelor study need to successfully pass the OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examination) examination to obtain their degree. This is an objective evaluation that tests both the student’s communication and clinical abilities and is used in many European countries. Simulation centres can be very useful for these types of evaluations.
Recording
Additionally, simulation centres often provide the ability to record training/evaluations. For training, recording provides a lot of value as it facilitates self-reflection, peer-reflection and feedback opportunities, helping trainees to really improve their capabilities. Moreover, if feedback and video sharing platforms like Videolab are also employed, then trainees can easily share their recordings with other members of their institution to obtain their feedback more easily. In these centres video recording is a powerful tool for education and we believe that more centres should ensure they implement it.
Now, let us go over some of the strengths and weaknesses of using medical simulation centres. This will create a more solid foundation to review possible improvements.
What are the advantages of using medical simulation centres?
From above, we can gather that medical simulation centres have many practical uses and offer several advantages for healthcare trainees and professionals.

Practice without risk
A big gain medical simulation facilities offer is a secure setting where healthcare students/ professionals can practice their skills and expertise without endangering actual patients. It allows for little or no patient risk. This allows them to gain experience and confidence when handling complex medical situations before encountering them in real life.
A paper written by students themselves communicates the satisfaction of simulation training is very high and argues the importance examining in simulated environments has on the practical application of knowledge. (Abas, T., Juma F. 2016. National Library of Medicine)
Medical students, who are the target of simulation training believe it aids their clinical decision making and positively benefits their confidence and autonomy.
Flexibility and Feedback
Simulation-based learning can be set up and repeated as often as required. It can be carried out with fewer limited resources or in amazingly high technology simulation centres. Simulated environments can be completely tailored to meet the needs and adapt to suit beginners, specialists and everyone in between to adjust and accommodate different learning styles.
Moreover, feedback can be given to students immediately, enabling them to pinpoint exactly what went well or poorly and how to improve. Peer review, video feedback and debriefing tools are all essential components of this learning experience. (TAPD. 2017)
Such debriefing tools can include Videolab, a powerful tool used for clinical assessments allowing numerous metrics for self reflection and trainer feedback.
Teamwork and communication
Simulation training gives healthcare students the opportunity to practice their teamwork and communication skills in a controlled setting. This is crucial in high-stress situations as the success of the patient care process depends on effective teamwork and clear communication with everyone involved. Read more on the importance of communication skills in healthcare environments in this blog post.
Reduced legal costs
By allowing healthcare students to practice in a simulated environment essentially helps reduce costs. Simulation centres can assist lower costs related to medical errors, malpractice lawsuits, and additional training required to correct errors made in real-life circumstances.
Medical practitioners’ competencies are improved and in return, improve patient safety and reduce healthcare costs. (IDSMED. 2018)
Medical simulation centres are necessary to service many different skills in training. But, it is very important to look at both sides of the coin, what disadvantages do they have? And lastly, what can we do to improve medical simulation centres?
What are the disadvantages of using medical simulation centres?
In this section we will go over some of the problems that come with using medical simulation centres.
Costs
The high costs associated with medical simulation centres pose a significant disadvantage. These costs can be divided into five areas: operational, administrative, maintenance/reparation, installation, and equipment costs. A deep dive in these costs can be found in these papers Archana et al. (2021) and Senvisky et al. (2022).
Equipment costs
Starting off with the latter, equipment costs comprise the costs that come with purchasing the equipment required to simulate medical procedures. Obviously, these costs vary a lot depending on factors like how advanced the medical equipment you are purchasing is or how many different medical procedures you are trying to replicate. Some examples of medical equipments present in these simulation centres include:
- High-fidelity adult patient simulators.
- High-fidelity birthing mannequins
- Surgical simulators
- High-fidelity neonatal, infant and child mannequins.
- Ultrasound machines.
- Radiology equipment.
Moreover, other non-medical equipment used in simulation centres also contributes to equipment costs, including:
- Recording and other audio visual equipment.
- Heating, ventilation and air conditioning.
- Safety systems like fire alarms.
- Lighting.
Installation costs
Installation costs refer to the cost of transporting, installing and setting up the equipment in the simulation centers. These costs can be quite expensive for heavier or more advanced equipment that requires more specialized technicians to set up.
Maintenance/reparation costs
These costs include the costs of maintaining and repairing all the installed equipment. Once again, obviously they depend on the amount of equipment that is and how often these equipment require maintenance. Additionally, the maintenance/reparation costs depend on the frequency of use and reliability of the equipment.
Administrative costs
This comprises a lot of costs. For example, costs include salaries of instructors, technicians, and other employees. Moreover, these can also include the costs of creating schedules for the use of the simulation centers (e.g., timetables for simulation classes or exams).
Operation costs
Finally, operation costs are comprised with the costs that come with having the centers in operation. For example, operation costs include the expenses of utilities such as electricity, gas, and water
All these different types of costs can add up to make setting up a simulation centre a very expensive endeavour. In Archana et al (2021), a high-end medical simulation centre was set up in the Mysuru Hospital in South India. The total cost of this centre added up to 3 million dollars. This included the cost of skill trainers, high-fidelity mannequins, and advanced surgical simulators. Thus, this serves as an example of why the costs of centres is one of the main disadvantages of them.
Example of the costs of a medical simulation centre
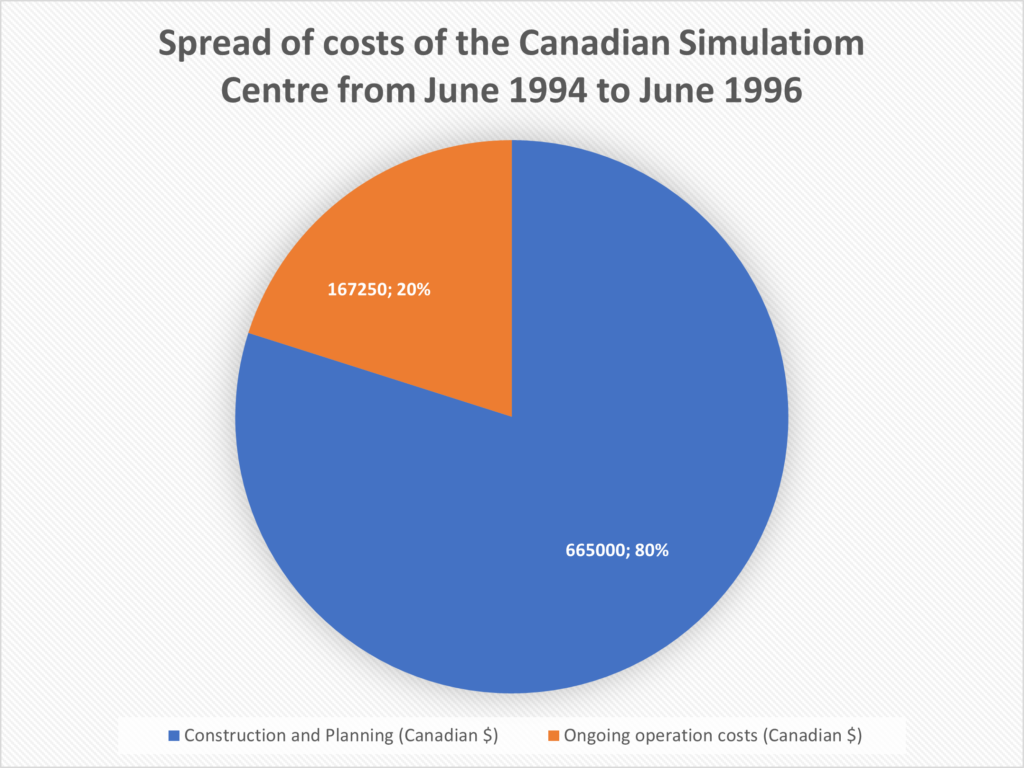
The chart above shows the spread of costs of the Canadian Simulation Centre at the Sunnybrook Health Science Centre of University of Toronto, from June 1994 to June 1996 (Kurrek & Devitt, 1997). The costs over these two years, as can be seen above, were 80% due to construction and planning and 20% due to the ongoing operations costs. The construction and planning costs were 85% due to capital equipment purchases and 15% due to salary support. Thus, in this case the installation and equipment costs summed to $565,250. Moreover, the ongoing operation costs consisted of the net costs of ongoing education and research activities (3.35 days/week), 65% of it can be attributed to salary support. This goes to show how expensive simulation centres can be, which is a disadvantage of using one.
Limits in medical training
The other main disadvantage of medical simulation centers comes with the limits they have in terms of training medical professionals. These limits can be separated into three main areas.
Limited realism
Simulation centers offer advanced equipment that imitates real-life scenarios, but the realism is limited, especially with low or mid fidelity equipment such as mannequins. Thus, medical trainees cannot fully prepare to do procedures on real patients. Therefore, it is crucial to use high fidelity equipment to practice for real-life medical situations. However, this is not to say that low fidelity or mid fidelity equipment cannot be used to build knowledge and competence, as mentioned in this blog post.
Limited scope
Medical simulation centers are limited in simulating various medical procedures. Thus, having a medical simulation center will not guarantee that medical trainees practice every different medical procedure they require. Therefore, it is important to develop simulation centers with good knowledge of the essential medical procedures that trainees must know. In that case, trainees will at least learn properly how to do essential procedures. If more budget is available, simulations for other scenarios can be added.
Limited patient interaction
Even though simulation centres may act as powerful tools to learn medical procedures, they can still lack the ability to teach trainees how to interact with patients. Developing communication skills through role-playing or by repeated interactions with patients is another crucial component of healthcare. Therefore, it is very important that medical simulation centres should not focus solely on clinical training. They should also focus on developing soft-skills to improve doctor-patient interactions.
All the limits posed above serve as a disadvantage of using medical simulation centres. Therefore, it is very important that they are considered when developing centres to try and work around them. Allocating more budget to the centre can help but this is not necessarily the only solution.
How can you be more efficient in your simulation centre
Tip 1: Focus on software rather than hardware. Avoid hard coded lessons, but look for connected devices that can load lots of different scenarios and can easily be updated in the future.
Tip 2: Maximise the use of your resources, do reviews and debriefings on a cloud platform so the rooms free up for more simulations, and there is no need for a debriefing room. The content of the session can be shared and reevaluated.
Tip 3: Avoid vendor lock-in. Vendor lock-in refers to a situation in which a customer is dependent on a particular vendor for products or services, and cannot easily switch to another vendor without substantial costs or inconvenience. It typically occurs when a vendor uses proprietary technologies which make it difficult for a customer to use the same products or services with a different vendor.
How to use Videolab and Cloudcontrol to make your simulation centre more efficient….
What is Videolab?
Videolab is a privacy-compliant video sharing platform where you are able to record patient interactions in a GDPR-safe environment.

Trainees record their simulated consultation, real patient consultations, or peer consultations, which are immediately encrypted and can be safely uploaded to the system. Trainees are then able to go back and watch this recording, reflect on their performance, make time fragmented comments or ask questions. These recordings are then shared with pre approved assessors to mark and evaluate. Secure collaboration also allows trainees to securely share the recording with peers and receive feedback from multiple different sources. Videolab can specifically address the issue when accessing a trainee’s skills as it allows for a complex and diverse evaluation environment.
Videolab is a MedTech solution that allows for secure healthcare training, with Cloudcontrol it is particularly suited to improve medical simulation centres.
What is Cloudcontrol?
Cloudcontrol is a tiny device that integrates with your recording hardware into the Videolab cloud. One device can control all cameras and users at any given location, even in complex multiple room simulation/ skills lab setups.
Architecturally it follows edge computing principles by bringing the power of the cloud into your hospital.
How does Cloudcontrol improve medical simulation centres?
Cloudcontrol software can enhance the intelligence, power, and flexibility of your hardware, and offers pre-approved users convenient access to powerful control panels.
Access to experts everywhere
Cloudcontrol’s video recording capabilities automatically upload to the Videolab allowing for offsite and asynchronous feedback.
This provides convenient access to experts everywhere, allowing more healthcare professionals to benefit from the resources and expertise available. (all must be given access by the administration.) The Videolab platform is user-friendly, with feedback given as easy as logging in and watching the recording shared with you.
The system is also very robust, with the ability to continue recording locally if the internet connection is lost, ensuring that no data is lost during training. Overall, Cloudcontrol software can greatly enhance medical simulation centres and provide healthcare professionals with the necessary tools to improve their skills and knowledge, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Eliminates expensive and high maintenance hardware
As mentioned above, users can access powerful control panels (with pre-approved user access), this enables them to control the simulation environment without the need for specialised hardware. Therefore, instead of relying on expensive hardware for video recording, the software records videos automatically and uploads them to the cloud for storage and easy access.
By eliminating the need for high-maintenance hardware, medical simulation centres can save significant costs in hardware acquisition, maintenance, and upgrades.
This would allow medical simulation centres to invest where needed, giving them more leeway on limitations mentioned above. They can invest in high quality simulation equipment, making the experience more dynamic and realistic for students. Finally, using Cloudcontrol, simulation centres can have more flexibility and scalability, without the worry of hardware limitations. CloudControl provides a cost-effective and reliable alternative to expensive and high-maintenance hardware.
Improves the security of simulation centres
Storing confidential patient videos or information off the cloud produces a privacy threat, it could be shared with the wrong people or left on the wrong device. Before considering recording patient interactions, read this blog post on GDPR compliance and limitations.
Cloudcontrol uses Videolab´s strong identification system onsite. Meaning, Cloudcontrol intercepts and encrypts the camera and microphone stream on the hardware level, which also assigns ownership rights at the source. This extends the protection of the Codific Secure Vault in each simulation room set up. Effectively minimising external threats and significantly reducing the potential for human error.
Assigning ownership from the source eliminates any confusion and mistakes around videos, compared to the alternative; with recording equipment, consultations get recorded externally and are assigned ownership later on, meaning there is a short period of time in which said video has no record and can be lost.
How do universities use Cloudcontrol to improve their medical simulation centers?
In the Netherlands, the Universities of Groningen and Maastricht are already using Cloudcontrol and experiencing the benefits of it.
In Maastricht, the Faculty of Health, Medicine and Life Sciences uses this device to optimize recordings in their skills lab, where they use simulation patients to train prospective doctors. This allows them to have easier access to experts, reduce costs of hardware and improve the security of their simulation centers. You can read more about it here.
Similarly, the University Medical Center Groningen experienced similar benefits as they chose to implement Cloudcontrol in all their departments, becoming the biggest deployment of this technology until now. Additionally, for this deployment we even developed a new server infrastructure, called the multi tenant infrastructure. This meant that the UCMG could have multiple instances of Videolab and Cloudcontrol under the same server, each with their own look and feel.
Who developed Cloudcontrol and what other applications do they offer?
Codific is a team of security software engineers that leverage privacy by design principles to build secure cloud solutions. We build applications in different verticals such as HR-tech, Ed-Tech and Appsec. Secure collaboration and secure sharing are at the core of our solutions.
SARA is used by top HR-Consultants to deliver team assessments, psychometric tests, 360 degree feedback, cultural analysis and other analytical HR tools.
SAMMY Is a Software Assurance Maturity Model management tool. Thus, it enables companies to formulate and implement a security assurance program tuned to the risks they are facing. That way other companies can help us build a simple and safe digital future. We also use SAMMY for Videolab and Cloudcontrol.
We believe in collaboration and open innovation, we would love to hear about your projects and see how we can contribute in developing secure software and privacy by design architecture. Contact us.