Updated: 2 April, 2024
What is Patient-Centered Care (PCC)?
The most crucial skill for a health practitioner is reportedly good communication. Effective communication depends on the therapist being confident that they have accurately understood and noted the needs of the patient in order to deliver individualized care. In order to identify patients’ true needs and respond appropriately by providing specialized care, health practitioners must have a thorough understanding of patients’ thoughts, feelings, and experiences. In this article we will be talking about Patient Centered Healthcare.
A patient centered approach is increasingly seen as essential for clinicians to provide high-quality care, built to ensure the patients wellbeing and understanding the situation that they are in by communicating. This way the patient knows what diagnosis they have and what they are being given as treatment, and can effectively give informed consent to the treatment.
All healthcare decisions are guided by the needs of the individual and the expected health outcomes in patient-centered care models.
Key takeaways:
- Patient centred care is a practice in which patients actively participate in their own medical treatment in close cooperation with their health professionals.
- Patient-centred care includes both empathy and patient-focused communication.
- There are eight dimensions of patient centred care: 1) Patients’ preferences 2) Information and education 3) Coordination 4) Emotional support 5) Physical comfort 6) Family and friends 7) Continuity and transition and 8) Access to care.
- Patient centred care can improve patient satisfaction, healthcare outcomes, and organisation reputation to name a few.
Dimensions of Patient Centered Healthcare
Patient-centered care includes both empathy and patient-focused communication. However, numerous studies show that during medical school, doctors’ capacity for empathetic communication declines. Communication training has a proven track record of enhancing interpersonal abilities, empathy, and patient-centered communication. By instructing clinicians in patient communication and empathy, it is important to improve patient-centered treatment.
Patient Centered Healthcare (PCC) has 8 dimensions.
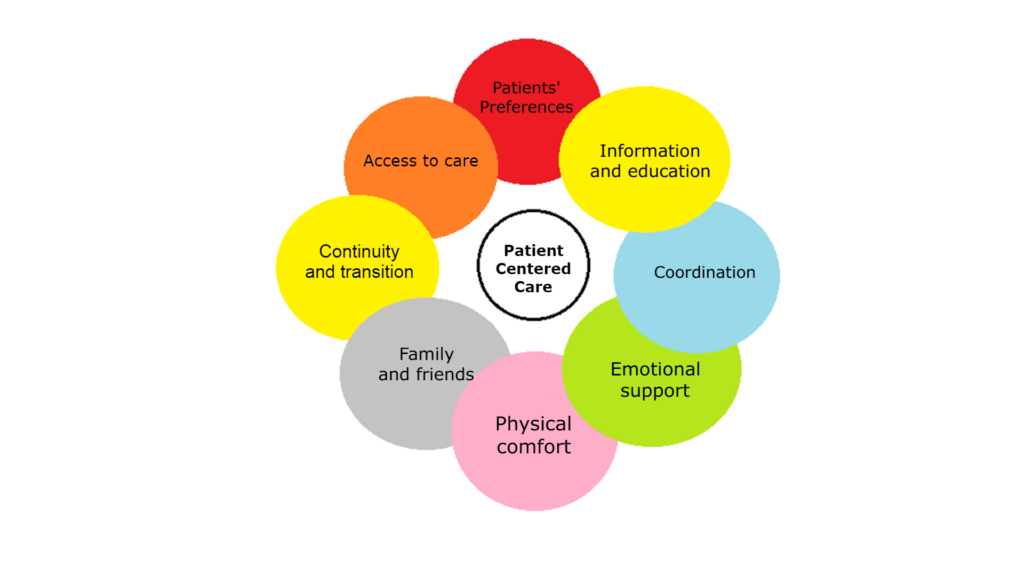
-
- Patients’ preferences
To identify the determinants of patient preferences for participation in medical decision making. - Information and education
A process of discussion between you and your healthcare professional called informed consent frequently results in agreement or authorization for care, treatment, or services. Before surgeries and treatments, the patient has the right to information and inquiries. - Coordination
Care coordination is the deliberate organization of patient care tasks and information sharing among all parties involved in a patient’s care in order to provide safer and more efficient care. - Emotional support
It is crucial to actively listen without passing judgment so that the patient can feel heard and safe. Find out how they prefer to be emotionally supported and acknowledge their feelings. While some patients might prefer a more proactive approach, others might just want you to listen. - Physical comfort
Patients are more likely to recover more quickly and have better health outcomes if they are comfortable. Negative surroundings prevent healing. - Family and friends
According to studies, having supportive relationships both makes us feel better mentally and acts as a powerful barrier against mental diseases. - Continuity and transition
To make certain that the patient-centered care team participates constructively in ongoing healthcare management with a view to achieving a common objective of high-quality medical treatment. The continuity of care encourages patient safety and ensures long-term quality of care. - Access to care
The patient can schedule a timely appointment with a licensed healthcare professional. It is crucial to improving health outcomes and managing long-term medical expenses.
- Patients’ preferences
Why is Patient Centered Healthcare so Important?
Patient satisfaction
Firstly, patient satisfaction is connected with how well a healthcare service satisfies a patient’s expectations for care.
Patient-centered care initially raises patient satisfaction rates by taking into consideration patients’ unique health goals and preferences and incorporating them into their own treatment along the way.
Improved organization reputation
Patients who are being treated well and that are satisfied will write reviews on your organization online. It is easier than ever to leave reviews and it is increasingly common to have a peek at the reviews prior to contact.
Moreover, a crucial element of a hospital’s good reputation is the patient view that it is a safe clinical setting with few errors.
Improved results
Years of research have shown that when patient values and preferences are given priority, patients are more engaged in treatments, which improves health outcomes. Patient-centered care is being implemented in hospitals and practices, which report:
- Lower rates of ER visits.
- A reduction in the use of healthcare resources.
- More contented patients, families, and care staff.
- Quicker recovery.
- Better health results.
Real-life Case Examples
Some real-life case examples of when Patient Centered Healthcare has worked are:
- The Joslin Diabetes Center in Boston, Massachusetts, is a world-renowned institution that provides comprehensive care for people with diabetes. The center has implemented a Patient Centered Medical Home (PCMH) model, which is a team-based approach that coordinates care across different providers and settings. The PCMH model has improved patient outcomes, such as reducing hospitalizations, emergency visits, and complications, as well as increasing patient satisfaction and engagement.
- The Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, is a leading academic medical center that offers a wide range of specialty and primary care services. The clinic has adopted a PCC philosophy, which is based on the principles of respect, compassion, collaboration, and empowerment. The PCC philosophy has enhanced the patient experience. Includes improving access, communication, and decision making, as well as fostering a culture of innovation and excellence.
- The Geisinger Health System in Danville, Pennsylvania, is a large integrated health care organization that serves more than 3 million people in 45 counties. The system has developed a Patient Centered Accountable Care (PCAC) program, which is a value-based payment model that rewards providers for delivering high-quality, low-cost care. The PCAC program has achieved positive results, such as lowering costs, improving quality, and increasing patient loyalty and trust.
How to Improve your organizations’ Patient Centered Healthcare
There are PCC frameworks designed to constantly improve patient satisfaction. One example of which, that was developed and made by The British Columbia includes both principles and regular practices to follow.
The four principles of patient centered care
- Dignity and Respect
This principle emphasizes the need of actively listening to patients and their families as well as respecting their decisions. This is accomplished by incorporating the values, beliefs, and cultural norms of the patient and family into care plans and care delivery.
- Information Sharing
This approach is based on collaboratively sharing timely, accurate, and comprehensive information about decisions to be made with patients and their families, as well as validating with them what they have heard and understood. This supports the patients’ and families’ ability to make an informed choice.
- Participation
Encouragement and support are provided for patients and their families to participate in care and make well-informed decisions, to the extent they are comfortable with and desire. The International Association of Public Participation’s spectrum of engagement (IAP2) is utilized to determine the appropriate level of involvement. The variety of engagement options includes informing, consulting, involving, collaborating, and empowering.
- Collaboration
There are substantial opportunities for patients and their families to interact with healthcare professionals and leaders along the continuum of quality improvement, policy and program formulation, implementation, and evaluation. This encompasses the potential for patient and family involvement in the design of healthcare facilities, the reform of the healthcare system, professional education, and the provision of care.
The four practices of patient centered care.
- Organization Wide engagement
An organization’s leadership should show their commitment to patient-centered care ideals in both their words and deeds.
- Workplace cultural renewal
Developing a culture of patient-centered care is crucial, and healthcare professionals and employees play a vital role in this process. A move from the “medical model” of care—which provides information, direction, and expert decision making—to a model of care where the patient is a partner in making care decisions is necessary to create a culture of patient-centered care. For health care providers to engage in patient-centered care activities, they must believe they have the organization’s support.
Patient-centered care principles must be taught to healthcare professionals and practiced on them in order for them to apply them in their daily job.
- Balanced Patient-Provider relationships
Patients are in need of assistance in the patient-provider relationship, and providers have the skills and background that patients require. Due to this, it is necessary to overcome the natural power disparity between patients and physicians.
- Tool Development
Lastly, the creation of tools to help the organization place the needs of patients and families at the center of care can enhance the goal of patient-centered care. This includes putting the patient’s voice at the heart of program and service planning, delivery, and evaluation.
Current best practices in patient centered care development
In some places patient centered care is deeply integrated into the way medical professionals are trained. One such place is The Netherlands where they use Videolab to develop patient centered care skills and mindsets.
With Videolab students can upload simulated consultations, peer consultations, or real patient consultations. The Videolab platform encrypts consultation videos at all stages of the process, and it allows for the recording of patient contacts in a GDPR-compliant manner.
Following that, the students can view the recording, assess their performance, and add time-fragmented comments or inquiries. Then, these recordings are accessible to pre-approved assessors for marking and evaluation. Thanks to secure cooperation, students can safely share the tape with others and receive feedback from various sources. Videolab can accurately address the issue of developing emotional intelligence because it can offer a complex and dynamic evaluation environment.
Who makes Videolab and why?
Codific is a team of security software engineers that leverage privacy by design principles to build secure cloud solutions. We build applications in different verticals such as HR-tech, Ed-Tech and Med-Tech. Secure collaboration and secure sharing are at the core of our solutions.
SARA: Top HR-Consultants use it to deliver team assessments, psychometric tests, 360-degree feedback, cultural analysis, and other analytical HR tools.
SAMMY Is a Software Assurance Maturity Model management tool. It enables companies to formulate and implement a security assurance program tuned to the risks they are facing. That way other companies can help us build a simple and safe digital future. Obviously our AppSec program and SAMMY itself is built on top of it.
We believe in collaboration and open innovation, we would love to hear about your projects and see how we can contribute in developing secure software and privacy by design architecture. Contact us.

References:
The British Columbia Patient-Centered Care Framework. (n.d.).
Available at: https://www.health.gov.bc.ca/library/publications/year/2015_a/pt-centred-care-framework.pdf.
