Updated: 2 April, 2024
“Individual commitment to a group effort – that is what makes a team work, a company work, a society work, a civilisation work.” – Vince Lombardi
Key takeaways
- There are six categories that fit inside of inter professional collaboration that must be achieved.
- There are multiple barriers that must be addressed to achieve efficient long term results.
- Case studies, policies, leadership programs and more help implement inter professional collaboration.
- Videolab provides you with an easy tool to measure and improve students learning in these fields.
What is inter professional collaboration?
The World Health Organisation defines inter professional collaboration in healthcare as ‘multiple health workers from different professional background working together with patients, families, carers, and communities to deliver the highest quality of care’
According to a research paper published in the National Library of Medicine, explored various areas of clinical practice and extracted six categories that make up inter professional collaboration, 1) Patient-centred care 2) Inter professional communication 3) Participatory leadership 4) conflict resolution 5) transparency of duties and responsibility and 6) Teamwork.
The study points out that 5) the transparency of duties and responsibilities was the most prominent and is required for any collaboration. The research outlines that the integration of these competencies into the educational curriculum is essential to form effective inter professional collaboration. (source).
Why is inter professional collaboration important in healthcare settings?
Inter professional collaboration offers numerous benefits that contribute to improved patient care and healthcare outcomes. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved patient outcomes: collaborative teamwork allows caregivers to pool their knowledge, skills and expertise to provide comprehensive and patient centred care. This approach leads to a better exploration of diagnosis, improved patient outcomes, and higher patient satisfaction.
- Increased patient satisfaction: Healthcare providers typically provide patients involved in inter professional collaboration with more patient-centred care (blog here), making them feel included in their health journey. Additionally, inter professional collaboration investigates more avenues of diagnosis and increases positive outcomes.
- Patients start treatment faster: reducing waiting times and communication delays through collaboration ensure timely access to important information and facilitating efficient treatment plans.
- Job satisfaction: working in a collaborative environment encourages a sense of belonging, shared purpose and mutual support.
- Increased efficiency: inter professional collaboration promotes efficient use of resources and streamlines healthcare processes. It minimised costs and optimised the delivery of care.
- Enhanced problem solving: complex healthcare issues require collaboration and problem-solving minds. Collaboration allows healthcare providers to brainstorm ideas, solutions and options following the same goal of patient health.
- Professional growth: healthcare providers working together on patient cases allows for professional growth by continuously learning from peers.
- Closes communication gap: closes the communication gaps between healthcare professionals and reduces errors of patient outcomes. (source). Working independently could lead to missed symptoms or miscommunication of patient needs. Whereas through inter professional collaboration, professionals engage on a personal level, exchanging ideas regarding patient treatment and cooperating to ensure consistent care.
Inter professional collaboration in healthcare provides several core benefits for the healthcare system showing the value of it within the healthcare setting. (source)
All of these reasons promote a more efficient healthcare system through communication and arguably, communication is one of the most important factors of patient care. Read more here for communication skills in healthcare.

What are some of the challenges?
In order to fully take advantage of the benefits inter professional collaboration offers, we have to incorporate and understand all of the categories it is made up of:
1) Patient-centred care
2) Interprofessional communication
3) Participatory leadership
4) Conflict resolution
5) Transparency of duties and responsibility
6) Teamwork
These categories in themselves are challenging and require continuous practice and interest. In order to be mindful of the challenges that come along with inter professional collaboration, we must first identify them.
Some of these include:
- Lack of time and training:
- healthcare professionals often work in fast-paced environments with demanding schedules. Time constraints can limit opportunities for team meetings, discussions and collaborative decision-making. This impacts the depth of inter professional collaboration. The same goes for training in these sectors. (source)
- Lack of clear roles:
- unclear understanding of roles and responsibilities among team members can lead to confusion and conflicts. Lack of clarity regarding each professional’s scope of practice and contributions will affect teamwork.
- Communication barriers:
- differences in professional language, terminology and communication styles can hinder effective collaboration.
- Hierarchical structures:
- Traditional hierarchies within healthcare settings can create power differentials that affect open communication and equal participation among team members.
- Professional resistance:
- Skills to deal with conflict and emotional stress can be difficult to manage. Students are taught to practise communication when dealing with difficult patients. However, there is much less practice on how to deal with challenging colleagues. (source)
- Some healthcare professionals may resist inter professional collaboration due to lack of understanding of benefits. Foresting a culture that values collaboration can be challenging.
- Organisational barriers:
- business structures, policies and practices that do not support collaboration can impede its implementations. Fragmented care delivery systems, lack of interdisciplinary team training and inadequate resources are all factors to these.
- Conflicts:
- Diverse professional backgrounds, perspectives and approaches may lead to conflicts and disagreements within a collaborative team. Resolving conflicts and fostering a climate of mutual respect and trust is essential for this. (source)
Addressing these challenges requires a commitment to creating a supportive environment, establishing clear communication channels, promoting inter professional education, and addressing structural barriers within healthcare organisations. Overcoming these challenges can lead to improved patient outcomes and a more effective and patient-centred healthcare system.
Strategies to implement inter professional collaboration in healthcare
In healthcare settings, various initiatives, policies and educational programs should be put in place to aid the implementation of inter professional collaboration in healthcare. Firstly starting with Inter professional Education (IPE), which would integrate into students medical education and provide opportunities for students from different disciplines to learn together and engage in joint projects and simulations.
One of the categories that is seen as the biggest challenge in collaboration is “duties and responsibilities” (source), which is where Collaborative Practice Agreements would establish formal agreements that define the roles and responsibilities of professionals within a team.

Leadership development programs and inter professional training would provide a consistent platform for healthcare professionals to discuss patient cases, share knowledge and focus on preparing students with the skills of leadership, understanding and flexibility.
This practice could come together in the following models:
- Inter professional rounds and case discussions: conduct regular inter professional rounds or case discussions where students and assessors come together to discuss complex patient cases, share perspectives and develop integrated care plans.
- Interdisciplinary training and workshops: training programs and workshops that focus on improving communicable skills, conflict resolutions and shared decision making.
- Leadership programs: provide programs which emphasise the importance of a supportive organisational culture which strives off values such as teamwork, encouragement and recognised the contributions of all healthcare professionals.
All of the above should be implemented throughout a student’s curriculum over the years. Many areas should be continuously practised and updated on new discoveries and developments in medicine. In order to secure this, there should be an introduction of policies and guidelines at an organisational level. Quality improvement initiatives both through asking and engaging healthcare professionals and also as a requirement. All of these should contribute to the implementation of inter professional collaboration.
Finally, Evaluation and Feedback: training programs should implement mechanisms to regularly evaluate and provide feedback on inter professional collaboration efforts. This will allow for continuous improvement, identify any barriers and ensure ongoing commitment to improvement.
This is where Videolab would step in…
Many of the above areas should be continuously practised and updated on new discoveries and developments in medicine. In order to secure this, there should be an introduction of policies and guidelines at an organisational level. Quality improvement initiatives both through asking and engaging healthcare professionals and also as a requirement.
By implementing these strategies, hospitals and universities can create an environment that supports and enhances inter professional collaboration among healthcare providers. This ultimately leads to improved patient outcomes, enhanced healthcare delivery and a more cohesive and effective healthcare system.
How can you examine inter professional collaboration?
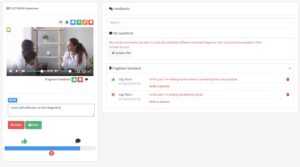
With the use of Videolab, a privacy-compliant video sharing platform, healthcare education offers significant benefits in fostering inter professional collaboration. By enabling students to record and share patient consultation, Videolab promotes a reflective learning approach. Students can review their own performance, identify areas for improvement, and engage in self-reflection. Moreover, they are then able to share these consultations with tutors, asking for feedback in a time-fragmented manner (see below).
This style of evaluation and assessment enhance inter professional collaboration by providing a shared platform for which students from different disciplines are able to engage in discussions and share insights, all in a safe and secure environment. Videolab provides a new resourceful and innovative way to assess inter professional collaboration in the healthcare setting.