Updated: 20 November, 2024
In the setting of healthcare, the emphasis has traditionally been on technical expertise and clinical knowledge. However, in recent years, the importance of soft skills in medical practice has gained recognition. These skills, encompassing communication, empathy, teamwork, and professionalism among others, are pivotal not only for fostering positive patient outcomes but also for shaping a well-rounded healthcare professional. Being able to master soft skills means you are able to answer the following sort of questions:
- Do you know how to help create a safe space for your frightened or anxious patients?
- Are you able to work well and clearly communicate with other team members in a stressful environment?
- Do you know how to make your patients feel comfortable in an awkward situation?
In this blog, we will take a closer look into the importance of soft skills in medical education. Some of the key soft skills for medical professionals, the challenges they may face in developing these skills and some ways to improve soft skills training. Additionally, we look towards the future, exploring how technology and med-tech tools can improve these skills.
Key takeaways:
- Strong communication and empathy in physicians lead to better patient relationships, higher satisfaction scores, and improved health outcomes.
- A study showed that empathetic doctors achieve better outcomes for patients, particularly in managing chronic conditions like diabetes.
- Teaching and assessing soft skills in medical education is challenging due to curriculum overload, subjective assessment methods, and resource constraints.
- Role-playing, continuous professional development, and technology such as Videolab enhance the teaching and assessment of soft skills in healthcare.
Why are soft skills important in medical education?
Soft skills are non-technical skills that relate to how you work and interact with others. Unlike hard skills, which are specific, teachable abilities or knowledge sets (such as medical procedures or clinical expertise), soft skills focus more on personal attributes and social abilities. Some essential soft skills include verbal and nonverbal communication, empathy, teamwork, leadership, and problem solving.
Soft skills are extremely important for medical professionals. When interacting with patients, family members and colleagues, soft skills are essential for building trust, fostering effective communication, and ensuring a compassionate and collaborative healthcare environment.
However, these skills may not come naturally to everyone and therefore must be deliberately taught and cultivated. Integrating soft skills training into medical education is crucial to prepare future healthcare professionals to meet the complex demands of patient centred care and teamwork in today’s medical landscape.
6 Key soft skills for medical professionals
Healthcare professionals require a diverse set of skills, and though it is difficult to highlight only a few of those set skills, here are six key soft skills that are particularly crucial for navigating everyday challenges and fostering positive patient interactions.
-
- Communication: Clear and compassionate communication with patients is essential for building rapport. Being able to explain complex medical information clearly, and actively listening to their concerns and questions.
- Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of others is essential to providing compassionate care. Many medical situations can be very intimate and personal, being able to both show empathy whilst delivering the whole truth delicately can be challenging for students. Empathy is also essential when communicating with a patient’s family or loved ones. Connecting on a human level and acknowledging fears, concerns and emotions enhance the quality of care.
- Teamwork: healthcare is often a collaborative effort, so working effectively with other professionals such as nurses, specialists, therapists and more is vital. In healthcare every decision can have a huge impact, therefore making sure there is synergy between all members of the journey can help achieve the best outcome.
- Stress management: The healthcare field can be demanding, so developing healthy coping mechanisms to manage stress is important for both personal well-being and patient care.
- Professionalism: Maintaining a professional demeanour, acting ethically, and upholding confidentiality are key aspects of professionalism allowing students to build a relationship with patients and colleagues.
- Problem solving & Critical thinking: Making sound decisions under pressure and analysing complex medical situations are essential.
By understanding, practising, and applying these soft skills, healthcare professionals can build trust, navigate complex situations, and ultimately deliver the best possible care.
Soft skills are key to patient centred care
“Physicians with well-developed soft skills are likely to earn higher patient satisfaction scores because of their ability to establish better relationships with patients and healthcare teams.” (ResearchGate. 2022)
Patient satisfaction is a crucial aspect of healthcare. When a doctor’s soft skills are lacking, patients may feel neglected and undervalued during their medical experience.
In a 2021 editorial published in the Journal of Patient Safety, it was revealed that communication errors played a significant role in 70% of adverse events in healthcare settings. Effective communication between office staff and clinicians is crucial for ensuring patient safety and satisfaction throughout the entire process—from intake to treatment to discharge.
Another study indicates that doctors with higher empathy scores have patients with better outcomes. Focusing on diabetic patients, the research found that those treated by more empathetic physicians experienced significantly lower rates of acute metabolic complications. This suggests a strong link between physician empathy and improved patient health.
Developing strong soft skills is essential for creating a positive and supportive environment where patients feel cared for and respected. For this reason, administrators and managers in clinical and medicine-adjacent settings must lead by example, demonstrating effective communication skills and actively promoting them at all levels of their organisations.
Challenges of soft skills training in medicine
Common challenges that occur when implementing soft skills training in medical education can be (but are not limited to):
- Curriculum overload: Medical education is already intensive, with students needing to master a vast amount of technical knowledge and clinical skills. Adding soft skills training can feel overwhelming and may be perceived as an additional burden. This challenge often leads to resistance from both students and educators who are concerned about time constraints and the potential dilution of core medical content. With this being said, medical institutions have shown a large increase in their focus on soft skills training.
- Assessment difficulties: Unlike technical skills, soft skills such as empathy, communication, and teamwork are inherently subjective and harder to measure. Traditional assessment methods, such as exams are not well-suited for evaluating these skills. This makes it difficult to provide objective, consistent feedback and to ensure that students are developing these essential competencies effectively.
- Lack of standardisation: How do you measure soft skills? There is often a lack of standardised curriculum and teaching methods for soft skills in medical education. Different institutions may have varying approaches, leading to inconsistencies in training and assessment. This lack of uniformity can make it challenging to ensure that all students receive comprehensive and equitable soft skills education.
- Resource constraints: Implementing effective soft skills training requires resources such as trained faculty, simulation tools, and time within the curriculum. Institutions with limited resources may struggle to provide high quality training and assessments, prioritising other skills training over soft skills.
These are very common challenges when approaching soft skills training in healthcare. By addressing these challenges with thoughtful and innovative solutions, medical education can effectively enhance the soft skills of future healthcare professionals. Below, find some solution suggestions.
How to improve soft skills training in healthcare
There are various strategies that organisations can implement to help improve soft skills training in their organisation. Some of which are mentioned below:
- Continuous learning and professional development: constantly participating in workshops and practical sessions that are focused on soft skills will help ingrain core training methodologies for future practice. It should also give students many opportunities to approach different situations where their emotional intelligence will have to adapt based on the scenario.
- Constructive feedback and self reflection: regular feedback sessions are necessary to offer valuable insights into areas needing improvement. When combined with self-reflection, these feedback sessions can become a very powerful tool for continuous growth, both professionally and personally.
- Role playing and simulation: role playing techniques create a safe environment to practise and improve soft skills without real world risks. By mimicking various scenarios, they provide the students with opportunities to learn, adapt, and prepare for challenging situations.
- Integrative curriculum design: by seamlessly integrating soft skills training into existing courses, organisations can ensure that these skills are developed alongside technical competencies. This can happen when students are doing case studies, or patient/simulated consultations, placing an emphasis on communication, empathy, and teamwork as well as the technical skills.
- Innovative assessment methods: implementing new assessment techniques such as peer reviews, reflective practice, and OSCEs specific for soft skills training can provide a more accurate evaluation of a student’s soft skills. These methods can offer valuable feedback and highlight areas for improvement.
- Standardised training programs: While standardised training methods of soft skills are a priority at many universities. Some medical schools may still need to ensure consistency across different departments and training.
Videolab in soft skills training
Videolab is a privacy compliant video sharing platform designed to extensively improve the learning experience. The platform enables students to safely record consultations (real patient or simulation consultations), upload them onto the platform and watch back, facilitating a reflective learning experience. Students are able to mark time fragmented feedback points to their video before sharing with assessors for additional feedback. Students can also share the recording with pre-approved peers for additional feedback from different sources. Videolab specifically addresses the issue when assessing emotional intelligence as it allows for a complex and diverse evaluation environment.
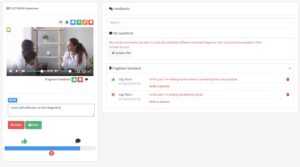
Highly respected universities use Videolab to assess their students’ soft skills when dealing with patient interaction. Take a read on how different Dutch universities use Videolab to improve skills development and training of students.
A tool such as Videolab provides a practical and scalable solution to developing and assessing soft skills. Videolab allows medical schools to use a multifaceted approach that leverages technology, standardisation, and innovative teaching methods.