Updated: 23 February, 2026
Introduction
In today’s rapidly changing healthcare landscape, video recording has emerged as an essential tool in many areas such as doctor patient consultations, operation room design and more. From boosting patient communication and medical education to generating innovative research, video recording technology is changing the way we deliver and experience healthcare. For example, a study conducted by Katherine Tayler surveyed seventy hospitals and reviewed 178 videotaped pediatric trauma cases. The study found that the use of universal precautions and personal protective equipment significantly improved, increasing from 14% of cases at the beginning of the program to 64% by the end of the review period. This significant improvement in safety practices demonstrates how video recording and review can directly enhance patient care and staff performance in critical healthcare settings.
This blog will explain the benefits for healthcare specialists and patients, while taking into account potential concerns regarding data privacy and patients comfort.
Key takeaways
- Surgical video recording enhances performance by enabling review, error identification, technique refinement, and knowledge sharing.
- Recording consultations improves doctor-patient communication by facilitating self-reflection and patient education.
- Video enhances medical education by providing a platform for training, feedback, and evaluation, improving communication skills and patient care.
- Video recordings provide valuable objective data for research by capturing the nuances of patient-provider interactions.
- Implementation takes time and requires requires consideration of both legal and ethical implications.
Benefits of Video Recording in Healthcare

Video recording in the operations room
Operating room video recording is transforming surgery by providing various benefits in education, quality assurance, and patient care.
Surgery teams are always analysing processes to identify instances of technical errors that don’t follow recommended practices. Video recordings help to identify areas for improvement by giving the doctors the opportunity to thoroughly study recorded surgeries. By reviewing the entire surgical sequence, teams can identify the root causes of errors and implement corrective measures to prevent it from happening again. This is especially useful because it gives them a clear and unbiased view on the process, which can often be difficult to achieve during an operation. Surgical teams not only benefit from videorecordings through analysing their own sessions but also from others. Conferences provide an ideal platform for surgeons to showcase innovative techniques through video presentations. This allows colleagues to observe and learn from their expertise and further gives surgeons from all over the world the opportunity to share their knowledge and experiences with the global community in a much more practical way.
(Source)
Doctor Patient consultations
Remotely
Another aspect showing the importance of videorecording in healthcare are the telehealth consultations, which got popular during Covid 19, but definitely also have its benefits for patients and practitioners in the current medical landscape since the distance between a doctors office or hospital and the patient’s home can be a big challenge too. If the patient is unable to move there it requires outside support from the local ambulance and even with assistance the transport is extremely painful with certain diseases.
In person
While remote consultations are necessary for some patients, many still prefer to visit the doctor in person. But even in person there are use cases for audio and video recordings, these records help the patient get a better understanding of their current medical situation since it allows them to review the consultation at their own pace. Being able to stop the recording and rewatch certain sections of the video helps the patient to understand his treatment plans, and facilitates active participation in their care.
Furthermore, recordings allow patients to share information with family members and caregivers, promoting a more collaborative approach to healthcare. For healthcare providers, recordings enable continuous improvement by implementing performance reviews and quality assurances, providers can identify areas for improvement in communication and patient education. This will lead in the long term to a better overall experience for the patients.
Advancements in Medical Education
Another area where video recordings are being used in medical education is in universities and other educational institutions. One of its use cases is the training of doctor patient communication, patient centered care and joint decision making. It is especially useful in the training of human interaction where the ability to see or hear the interaction is essential in understanding the interaction. Empathy is a recurring topic in many of these training sessions. Researchers at the University of Geneva found strong advantages of using video based feedback rather than direct feedback. Soft skills training is the most common type of training.
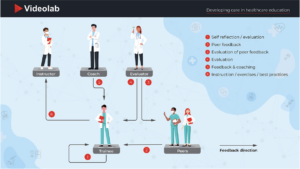
The Netherlands and Belgium are forerunners when it comes to innovative training methods, particularly in the field of communication training. ‘These are the documented use cases different universities are currently practicing:
1: Self reflection: A University of Leuven study found nearly 90% of students improved their communication skills through video recording, allowing them to record and annotate their performances.
2: Peer feedback: Trainees can review each other’s recordings to optimize learning. This peer feedback benefits both the giver (develops critical skills) and receiver (gets multiple perspectives).
3: Evaluation: For formal assessments universities rely on OSCEs or similar evaluation criteria. These can be recorded and reviewed through video, making the grading process more reliable and transparent.
4: Meta Feedback or Evaluation: In some cases the supervisors provide feedback on the peer feedback of trainees. ErasmusMC in Rotterdam uses this methodology in order to train the feedback giver.
5: Coaching: The main use case, along with self-reflection, is learning and development feedback. Trainers use fragment and overall feedback mechanisms to give more detailed and personalised feedback.
6: Instructor Initiated Videos: Shifts from trainee recording (use cases 1-5) to trainer-provided recordings for specialist training. Recording rare but crucial situations that happen in the hospital exposes trainees to more uncommon situations from a first person perspective and helps them in future decision making.
University of Maastricht
For example at the university of Maastricht in the skills lab, the students engage with simulation patients trained by the university, going through 28 scenarios across their four-year bachelor’s program. These simulations are being recorded for peer feedback, with students providing individual assessments before receiving collective feedback. Instructors also conduct top-down evaluations of at least three recordings per student, often accompanied by coaching sessions. Students can independently record their practice sessions with simulation mannequins or role-playing peers using video recording for self-reflection and optional peer feedback. Furthermore, video recordings are being used to enhance the performance of simulation actors.
Research
Videorecording is also widely used in research, offering the following benefits:
Video recordings provide a comprehensive and objective way to visualize clinical care, by capturing all aspects of a clinical encounter, including verbal and nonverbal communication, which can be difficult to capture accurately through traditional observation methods. This can be helpful for researchers who are studying complex interactions between patients and healthcare providers.
It allows researchers to verify their observations as they are able to review video recordings multiple times to ensure that their observations are accurate. This can be especially helpful for studies that are investigating subtle or nuanced behaviors.
Another area where video recordings are useful is to compare how patients and healthcare providers report their behavior compared to how they actually behave during a clinical encounter. This can help researchers identify areas where there may be discrepancies and adjust their findings accordingly therefore making studies more reliable and accurate.
Furthermore it can be used to analyze nonverbal communication cues, such as body language and facial expressions. These cues are difficult to spot in a live setting, where the clinician has to focus on different things at the same time. But it can provide important information about a patient’s or healthcare provider’s emotional state and understanding of the situation.
Legal considerations
Doctor-patient consultations rely on trust, which makes these interactions inherently sensitive.. This brings up the question if storing patient videos is legal?
To answer this question we have to look at the data protection regulations such as GDPR, HIPPA and CCPA. Storing data and therefore also videos of patients in a GDPR compliant way means that organizations handling the personal data of individuals in the EU and EEA must protect that data and respect the individual rights granted by the GDPR.
Organizations must comply with these two principles, in order to do this, they must follow the following rules:
- Obtain explicit, freely given, and informed consent from individuals before collecting, using, or processing their personal data.
- Only collect personal data that is necessary for the specific purposes.
- Protect personal data with appropriate technical and organizational measures.
- Allow individuals to access, rectify, erase, restrict, or object to the processing of their personal data.
- Allow individuals to withdraw their consent or exercise their right to data portability at any time.
- Report any data breaches to the relevant authorities within 72 hours.
- Appoint a data protection officer (DPO) if the organization is a public authority, engages in large-scale processing of special categories of data, or carries out large-scale monitoring of individuals.
- Keep detailed records of data processing activities.
If we follow the rules mentioned above and properly acquire consent, then recording patients is legal. Nevertheless, if you are interested in finding more about how to record, store and share videos in compliance with GDPR then please refer to this article.
Ethical Considerations
While the legal situation is quite clear in terms of measures institutions have to comply with, the ethical considerations are more ambiguous.
Even while complying with the best practices, video recording still introduces significant privacy risks. Accidental breaches can occur due to technical glitches, data security flaws, or human error. There are many instances where malicious actors were able to gain access to sensitive patient data for personal gain. Even with robust security measures, the risk of a breach cannot be entirely eliminated. Furthermore, unintended disclosure can occur through accidental sharing with unauthorized individuals. If an organisation intends to work with patients’ videos it is important to have a secure system in place that strictly follows data protection principles.
A big worry a lot of GPs have when introducing a video recording system to their organization is the implications on the quality of consultations. A study examining the impact of video-recording on GP consultations found that awareness of video-recording did not significantly influence the consulting behavior of four GPs, as measured by the TIMER coding system. It has to be mentioned that the introduction process takes time. For example, the study by Eeckhout found that over 60% of the GP trainees believed that patients felt uncomfortable during video-recorded encounters. It’s important to note that this was the trainees’ perception of patient comfort, not a direct measure of patient discomfort. While studies show the fear of implementing video systems in a clinic seems unfounded, doctors will likely initially feel uncomfortable being recorded. The right implementation process is key.

How Videolab Can Empower Your Healthcare Organization
Video recording offers a multitude of benefits for healthcare institutions, from enhancing patient care and education to improving research and staff performance. However, navigating the legalities and ethical considerations surrounding patient privacy can be a complex task. This is where Videolab comes in.
Videolab by Codific is a secure platform specifically designed for video recording in healthcare settings. The Videolab recorder is a flexible, and secure, recording app. It gives healthcare professionals the opportunity to make secure recordings no matter the place and time. The videos will not be saved on your devices but instantly uploaded to a secure cloud giving you full control over who and how long the access gets granted to other users.
The key speciality besides the multiple feedback functions is the privacy by design architecture to keep your data safe. You can read more about how we do this here, here and here. Following this design architecture is imperative to follow Article 25 of the GDPR.
At Codific, we believe that videorecordings are the future of healthcare and health education. Clearer communication, better understanding, and improved outcomes – It doesn’t have to be complex but it has to be safe. Therefore we believe in a simple and safe digital future.
